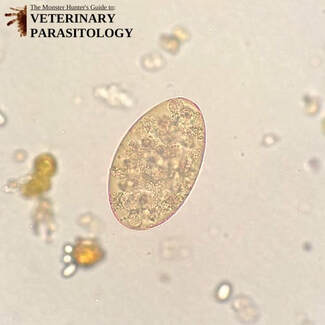
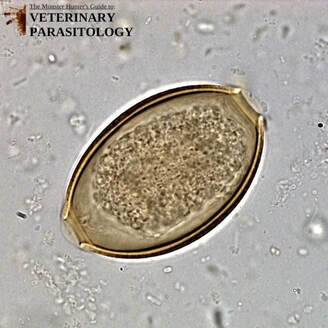
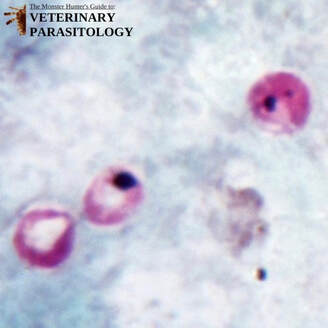
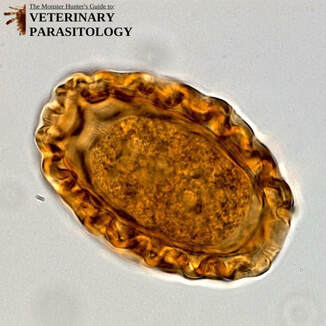
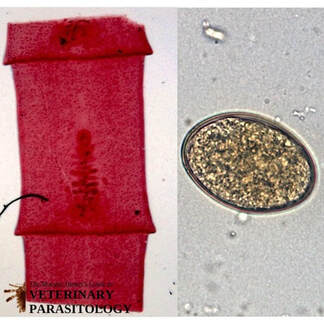
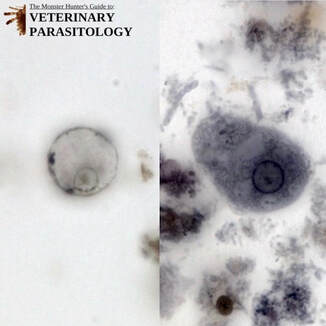
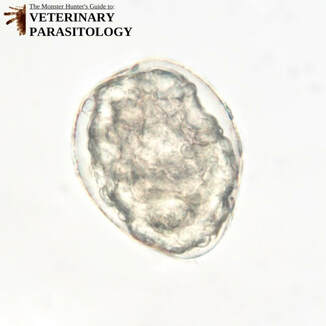
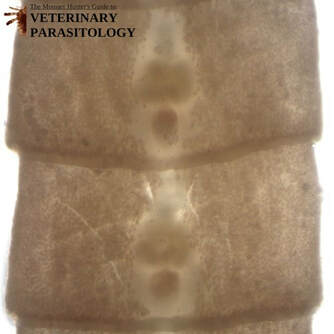
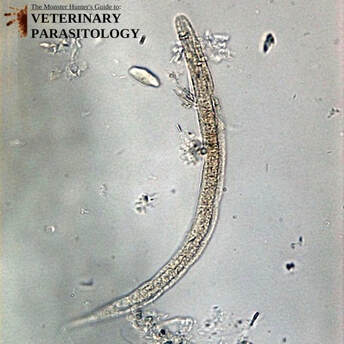
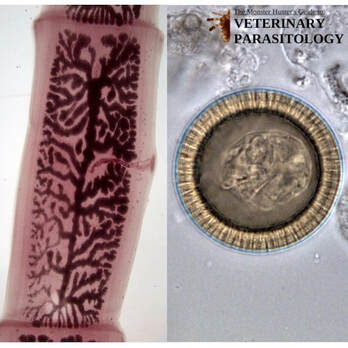
Ancylostoma spp.(aka., Hookworm) |
Method of Detection:
|
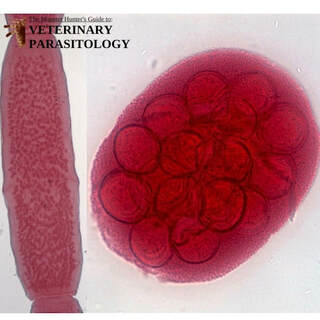
Baylisascaris procyonis(aka., Raccoon Roundworm) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
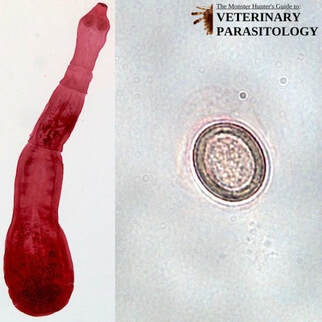
Cystoisospora canis(aka., Coccidia, Isospora canis) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
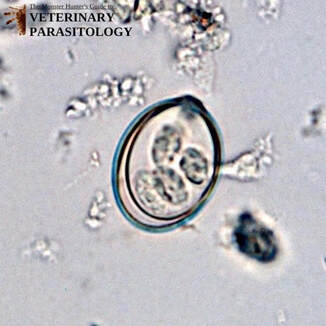
Cystoisospora ohioensis(aka., Coccidia, Isospora ohioensis) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Hammondia heydorni, Neospora caninum, or Toxoplasma gondii |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Nanophyetus salmincola(aka., Salmon Poisoning Fluke, Troglotrema salmincola) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
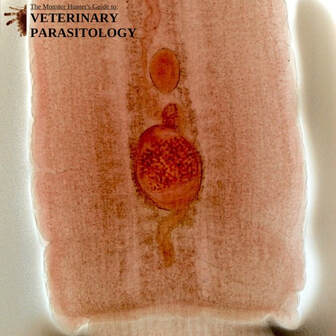
Paragonimus kellicotti(aka., Lung Fluke) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
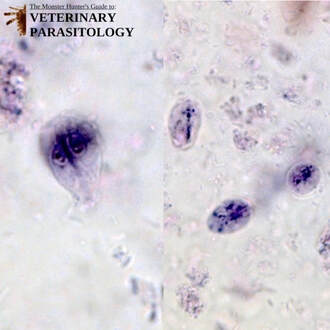
Pentatrichomonas hominis(aka., Pentatrichomonas felis, Trichomonas felis, Trichomonas intestinalis) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Physaloptera spp.(aka., Stomach Worm) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Sarcocystis spp. |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Spirocerca lupi(aka., Esophageal Worm, Spirocerca sanguinolenta) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Toxascaris leonina(aka., Roundworm, Toxascaris limbata) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Toxocara canis(aka., Canine Intestinal Roundworm) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Trichuris vulpis(aka., Whipworm) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Uncinaria stenocephala(aka., Northern Hookworm) |
Method of Detection:
Size:
|
Sources Cited:
- Zajac, Anne M., and Gary A. Conboy. Veterinary Clinical Parasitology. 8th ed. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. Print.
- Taylor, Mike A., R. L. Coop, and Richard L. Wall. Veterinary Parasitology. 4th ed. Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley Blackwell, 2016. Print.
- American Association of Veterinary Parasitologists. (2010). Retrieved 2019, from http://www.aavp.org.
- Palić, Jelena, Shannon J. Hostetter, Elizabeth Riedesel, Rebecca Richardson-Bill, and Julie Ann Jarvinen. “What Is Your Diagnosis? Aspirate of a Lung Nodule in a Dog.” Veterinary Clinical Pathology 41.1 (2011): 99-100. Web. 5 Aug. 2017.